From the Field to the Dashboard – Built by Experts, for Experts.
Discover What's Really Happening in the Steel Industry
Use the AI-powered search engine to analyze production activity, market trends, and news faster than ever before.
Try the Free AI Search EngineAsia Steel Market稳: Tariffs Impact Automakers, Plant Activity Dips
The Asian steel market remains neutral, but faces headwinds. News reports concerning automotive industry setbacks directly impact steel demand, though a one-to-one connection with observed plant activity levels cannot always be explicitly established. Specifically, General Motor’s sales increase in Asia is partially offset by tariff headwinds, as detailed in “GM boosts sales, takes $1.1bn tariff hit in 2Q“. The news articles mentioning Stellantis (“Milliardenverlust: Die Talfahrt von Stellantis hält an“) and Volkswagen (“Volkswagen: Gewinn von VW bricht im zweiten Quartal ein – Autobauer senkt Prognose” and “Gewinn von VW bricht um ein Drittel ein – Zölle kosten Autohersteller 1,3 Milliarden Euro“), indicate a potential broad-based reduction in automotive manufacturing output due to tariffs and related financial constraints and can therefore affect demand for steel.
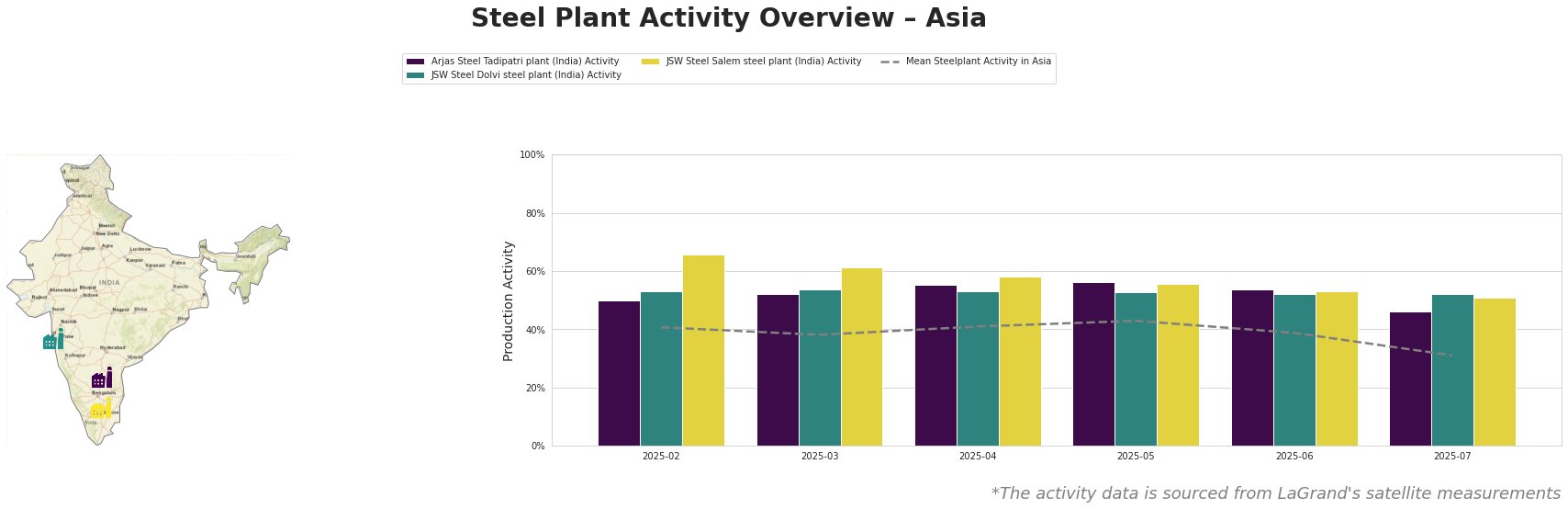
Across Asia, the mean steel plant activity decreased significantly to 31% in July, from 43% in May and 39% in June.
Arjas Steel Tadipatri plant, an integrated BF-BOF steel plant in Andhra Pradesh, India, produces 325 ttpa of crude steel, mainly finished rolled and semi-finished products such as bars, squares and rounds for multiple end-user sectors including automotive. The plant’s activity has shown a decreasing trend, from a peak of 56% in May to 46% in July. This 10% drop might be correlated with the automotive sectors’ headwinds as indicated in the news articles “GM boosts sales, takes $1.1bn tariff hit in 2Q“, “Milliardenverlust: Die Talfahrt von Stellantis hält an“, “Volkswagen: Gewinn von VW bricht im zweiten Quartal ein – Autobauer senkt Prognose” and “Gewinn von VW bricht um ein Drittel ein – Zölle kosten Autohersteller 1,3 Milliarden Euro“.
JSW Steel Dolvi steel plant, located in Maharashtra, India, operates as an integrated BF and DRI plant with a 5000 ttpa crude steel capacity. It utilizes both BF and EAF technologies, producing finished rolled and semi-finished products like wire rod, cold rolled, hot rolled, and galvanized steel for various sectors, including automotive. Activity at this plant has been relatively stable, fluctuating around 52-54% from February to June, with a slight decrease to 52% in July. While the news articles generally indicate a challenging environment for automakers, no explicit connection can be made to the JSW Dolvi plant’s observed activity levels.
JSW Steel Salem steel plant, an integrated BF steel plant located in Tamil Nadu, India, has a crude steel capacity of 1030 ttpa. It produces semi-finished and finished rolled products, including hot rolled bars and flats, catering to sectors like automotive. The plant’s activity experienced a gradual decline from 66% in February to 51% in July, a 15% decrease. This drop, similar to Arjas Steel Tadipatri, may be linked to the struggles reported by automotive manufacturers, as indicated in the news articles “GM boosts sales, takes $1.1bn tariff hit in 2Q“, “Milliardenverlust: Die Talfahrt von Stellantis hält an“, “Volkswagen: Gewinn von VW bricht im zweiten Quartal ein – Autobauer senkt Prognose” and “Gewinn von VW bricht um ein Drittel ein – Zölle kosten Autohersteller 1,3 Milliarden Euro“.
Considering the observed decline in steel plant activity, especially at Arjas Steel Tadipatri and JSW Steel Salem, coupled with the reports of financial difficulties and tariff impacts on automotive manufacturers, steel buyers should prioritize the following:
– Diversify supply sources for steel products, particularly bars, squares, and rounds, to mitigate potential supply disruptions in the Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu regions.
– Closely monitor inventory levels and adjust procurement strategies to account for potential delays or reduced output from affected plants.
– Negotiate contract terms that allow for flexibility in delivery schedules and pricing to manage uncertainty related to tariffs and production fluctuations in the automotive sector.