From the Field to the Dashboard – Built by Experts, for Experts.
Discover What's Really Happening in the Steel Industry
Use the AI-powered search engine to analyze production activity, market trends, and news faster than ever before.
Try the Free AI Search EngineDeclining Steel Production in Asia Signals Supply Challenges Amidst Negative Market Sentiment
Recent developments illustrate an increasingly negative market sentiment in Asia’s steel industry, driven primarily by operational challenges within key plants. Significant drops in satellite-observed activity levels correlate directly with the findings in “US details plans to take over PdV sales: Update,” highlighting a critical shift and potential supply disruption in the region.
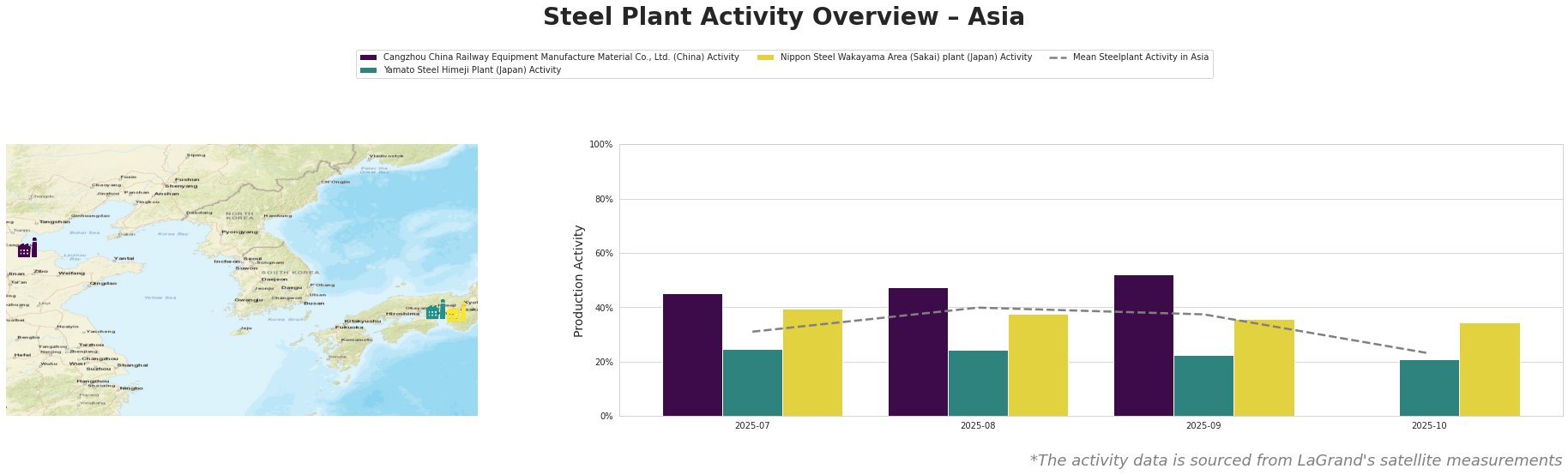
The mean activity across steel plants dropped significantly from 40% in August to just 23% in October 2025. Cangzhou observed a high of 52% in September but fell to inactive levels in October, aligning with operational issues raised in the aforementioned news. Yamato Steel and Nippon Steel reported a decline as well, where Yamato’s activity declined from 25% to 21%. These trends signal diminished production capacity and potential future supply constraints, particularly linked to affected infrastructure as noted in the news articles.
Cangzhou China Railway Equipment’s recent inactivity indicates critical operational challenges, likely exacerbated by developments related to the Venezuelan oil crisis impacting global steel supply chains. While it achieved a peak at 52% in September, the plant subsequently dropped to inactive status in October without a clearer connection to the external news reports. The facility relies heavily on integrated processes, with its primary output being high-quality structural materials.
Meanwhile, the Yamato Steel Himeji Plant, which operates via an Electric Arc Furnace with a capacity of approximately 1,495 tonnes, saw a significant activity drop from 25% to 21%. This decline could reflect broader economic tensions affecting the construction and machinery sectors.
Nippon Steel’s Wakayama Area experienced a modest decline but remained relatively better positioned than its counterparts, reaching 36% in October. Nevertheless, this figure suggests that even established plants are navigating reduced demand and operational challenges.
Given these observations, steel buyers should anticipate potential supply disruptions within specific regions, notably from Cangzhou’s operational lapses. It is prudent for procurement professionals to consider diversifying their sources beyond these affected plants. Continued monitoring of plant activities is essential, particularly as geopolitical dynamics evolve, notably surrounding the implications of the U.S. policy actions pertaining to Venezuelan oil.
Steel buyers should consider securing contracts with suppliers experiencing stable operations to mitigate risks tied to fluctuations in production capacity influenced by external geopolitical factors.