From the Field to the Dashboard – Built by Experts, for Experts.
Discover What's Really Happening in the Steel Industry
Use the AI-powered search engine to analyze production activity, market trends, and news faster than ever before.
Try the Free AI Search EngineAsia Steel Market: Activity Declines Amidst Fluctuating US Trade Flows
Asia’s steel market faces potential adjustments amid fluctuating US steel trade, though direct connections to regional plant activity are limited. Declining activity levels have been observed across key Asian steel plants, yet these trends cannot be directly linked to the provided news articles concerning US steel imports and exports, including “US steel imports up 11.6% in March 2025“, “US exports of plates in coil up 7.6 percent in March from February“, “US HRC imports down 11.5 percent in March from February“, and “US HRC exports up 28.2 percent in March from February.”
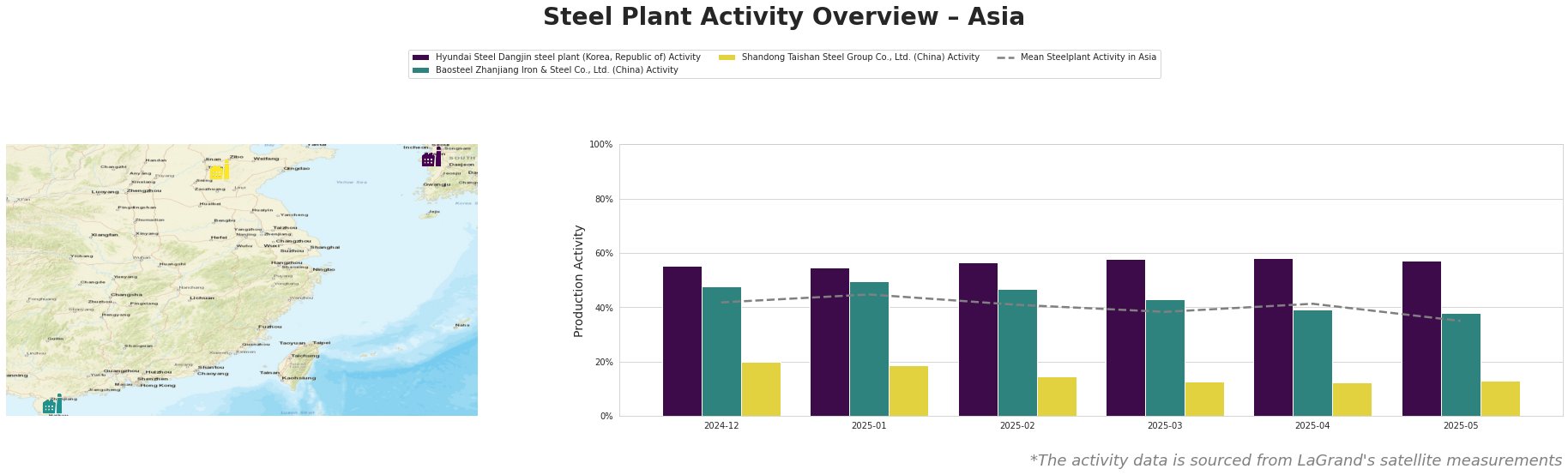
Observed plant activity shows a general downward trend in Asia. The mean activity across the observed plants decreased from 42% at the end of December 2024 to 35% by the end of May 2025.
Hyundai Steel Dangjin steel plant, a major integrated steel producer in South Korea with a crude steel capacity of 16.6 million tonnes per annum (mtpa), primarily utilizing basic oxygen furnace (BOF) technology alongside electric arc furnace (EAF) operations, maintained a relatively stable activity level. The plant’s activity fluctuated slightly, starting at 55% in December 2024 and decreasing to 57% by May 2025. This relative stability occurs while US HRC imports from South Korea have declined significantly (see article “US HRC imports down 11.5 percent in March from February“).
Baosteel Zhanjiang Iron & Steel Co., Ltd., a significant integrated steel plant in Guangdong, China, with a crude steel capacity of 12.5 mtpa based on BOF technology, experienced a decline in activity. Activity decreased from 48% in December 2024 to 38% in May 2025. This decrease contributes to the overall decline in Asian steel plant activity, but a direct correlation to the provided news articles regarding US steel trade cannot be established.
Shandong Taishan Steel Group Co., Ltd., an integrated steel producer in Shandong, China, with a smaller crude steel capacity of 5 mtpa, displayed the lowest activity levels and a downward trend. Activity declined from 20% in December 2024 to 13% in May 2025. As the plant produces hot rolled coil, cold rolled coil and stainless steel, and the US article “US HRC imports down 11.5 percent in March from February” indicates changes in the HRC sector, it could be speculated that the trends are linked, although there is no direct reference to this Chinese plant’s products.
Evaluated Market Implications:
The observed decline in average steel plant activity across Asia to 35% in May 2025, coupled with steady output at Hyundai Steel, suggests a potential shift in regional supply dynamics. The US’s reduced HRC imports from South Korea may contribute to the stable activity seen at the Hyundai Steel Dangjin plant, as the plant finds an alternative regional outlet for its HRC product.
Recommended Procurement Actions:
- Steel Buyers: Prioritize securing HRC supply contracts with Hyundai Steel in the short term. The plant’s consistent activity suggests a reliable source, particularly if the US HRC import restrictions remain in place.
- Market Analysts: Monitor the price differential between US-destined and regionally-destined HRC from South Korea. A widening gap could indicate increased regional supply and potentially more favorable procurement terms. Further investigate the reduced activity in Baosteel and Shandong Taishan Steel to determine if this is due to an oversupply in HRC from other suppliers, or due to planned maintenance, or perhaps even trade tariff implications or internal Chinese economic factors.